The Specialized Connective Tissue That Forms Our Teeth Is
2- Connective tissue proper. Glycolysis produces a total net gain of 8 ATP.
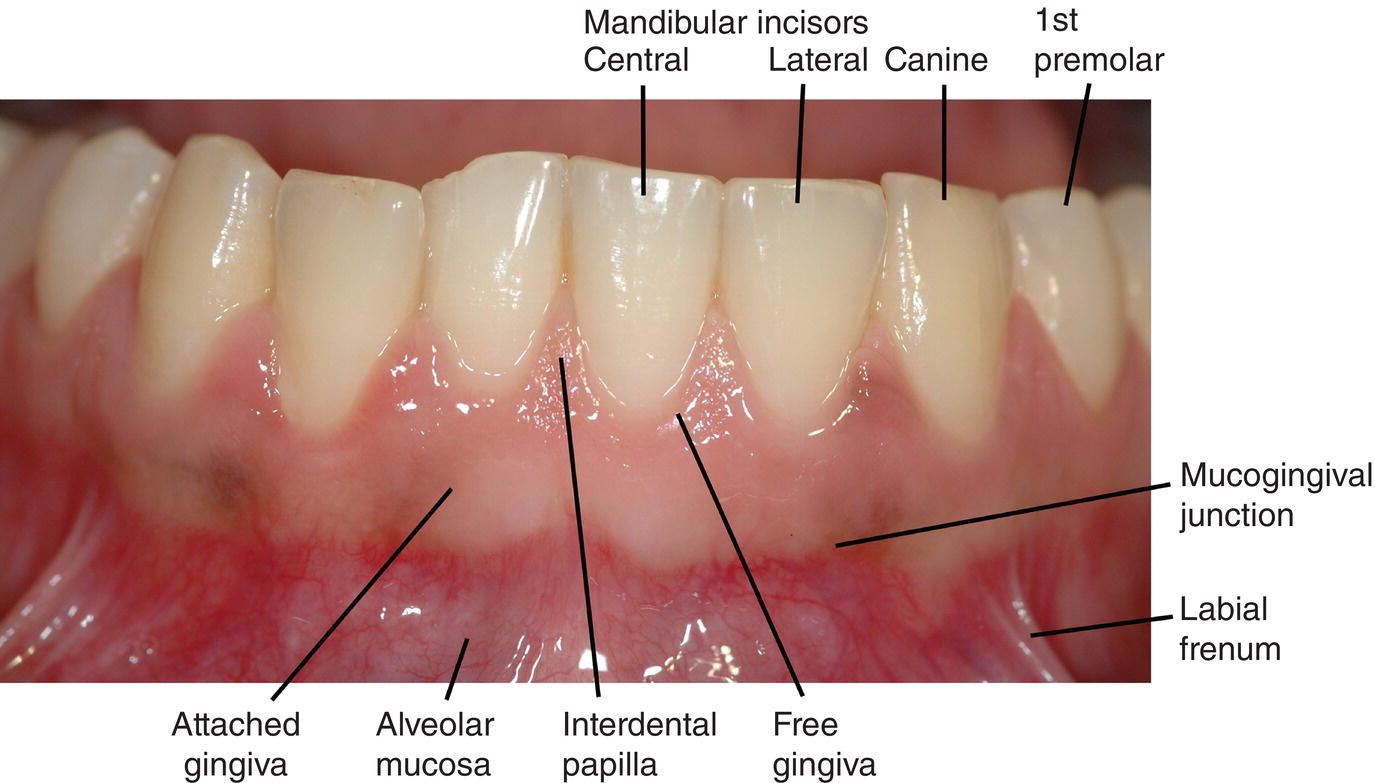
1 Oral Structures And Tissues Pocket Dentistry
This makes bone ideally suited to fulfilling its most recognized role within the body that of mechanical support.

. FORMS OF BONE TISSUE Spongy bone cancellous Compact bone cortical dense Has numerous spaces visible to the naked eye Outer casing appears as a solid mass More abundant in the body Accounts for 20-25 of bodys total skeletal mass Accounts for 75-80 of bodys total skeletal mass Consists of interconnecting bone fragments spicules. Specialized connective tissue in which the ground substance forms from a from SYSB 1106 at Virginia Tech. Loose areolar connective tissue.
Collagen fibres are the most widespread and made up of fibrous protein collagen. Unlike other connective tissues its extracellular components are mineralized giving it substantial strength and rigidity. Click again to see term.
Dense regular connective tissue. Elastic fibres form a network and can be stretched like a rubber band. Specialized connective tissue is the second type which has specialized cells.
Specialized connective tissue includes adipose blood bone cartilage and lymphoid tissue. A tough fiber found in the matrix of connective tissue. The Specialized Connective Tissue that forms our teeth.
3- Specialized connective tissue. Click card to see definition. Areolar connective tissue E.
Dense irregular connective tissue. The periosteum covers external surfaces of most bones and is divided into two distinct layersan outer fibrous and inner cellular layer Figure 2F. 5 The cells found in loose connective tissue that function in the production of heparin and histamine are.
Specialized connective tissue. Specialized connective tissue that has a main role of antibody production and the protection from disease and foreign microorganisms mast cells loose connective tissue cells that function in the production of heparin and histamine. The dense connective tissue making up the teeth is named.
The Krebs citric acid cycle produces for each of the 2 pyruvic acid molecules 14 ATP via electron transport and 1 ATP or GTP. Connective tissues contain three types of fibres. Click card to see definition.
Light brown in appearance. Types of connective tissue. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
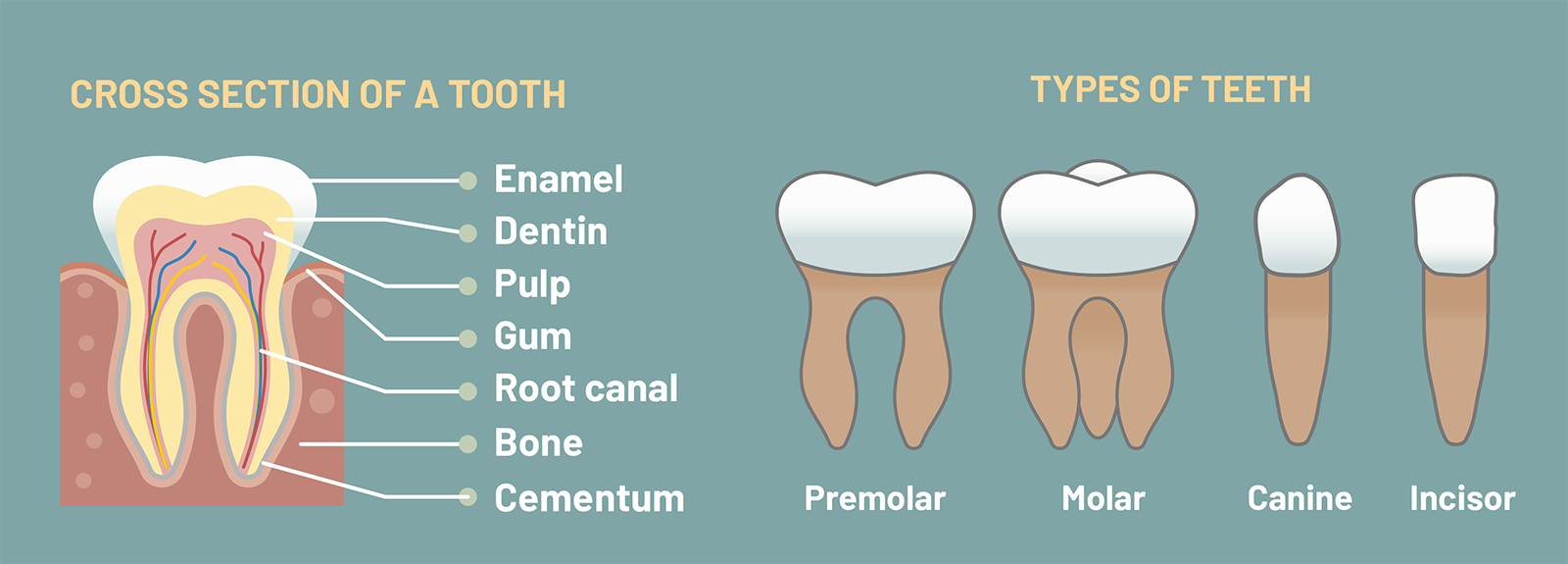
Mixed Connective Tissue Disease. Start studying Final 2. Cementum is a specialized connective tissue that can form throughout the life of from BIOLOGY 20 at M.
Mixed connective tissue MCTD disease is an autoimmune disorder with signs and symptoms of at least two different connective tissue diseases and the presence of an antibody known as RNP. There are many functions in the body in which the bone participates such as storing minerals providing internal support protecting vital organs enabling movement and providing attachment sites for muscles and tendons. Bone is a connective tissue containing cells fibers and ground substance.
The cellular or cambium layer is positioned in direct contact with the bone surface and is of particular interest as it contains mesenchymal stem cells MSCs which have. Found lining the ducts of certain glands and in mucous-secreting tissues. Tap again to see term.
5 In the anatomical position the body is. Cartilage that has a matrix with no fibers is called. Tap card to see definition.
Epithelial cells that are tall and rectangular. The chemical energy in the food calories is released and used to put together adenosine diphosphate ADP and phosphate PO4 to make ATP. Bone surfaces are covered by specialized connective tissues.
Therefore it consists of reticular connective tissue adipose tissue blood cartilage and bone etc. Connective tissue proper further divide into loose connective tissue and dense connective tissue. Areolar or loos connective tissue.
Standing erect face forward arms at the sides palms toward the front feet parallel Chp. Dense regular and dense irregular. Collagen fibres are flexible and have high tensile strength comparable to steel.
Tap card to see definition. Elastin fibers embedded in the matrix of this connective tissue give it the name ____ cartilage. Collagen elastic and reticular.
Forms the outer layer of bone and is very dense. 13 The most common signs and symptoms in patients with MCTD include Raynauds phenomenon swelling of the hands and. There are two subtypes of dense connective tissue based on the arrangement of the fibres.
What is above the gums is covered in a layer of white enamel which is secreted onto the dentin by special epithelial cells that make up the enamel organ. Dentin is closely related to Bone in structure but is harder and denser. Delicate thin membraned throughout the body.
Thus this summarizes the difference between connective tissue proper and specialized connective tissue. Bone is a specialized connective tissue consisting of cells fibers and ground substance.


No comments for "The Specialized Connective Tissue That Forms Our Teeth Is"
Post a Comment