Describe the Role of the Following in Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Following training at the two higher intensities but not the lowest intensity the accumulation of AMP and ADP and the depletion of phosphocreatine and glycogen during steadystate exercise were reduced more following the 60 min day 1 as compared to the 30 min day 1 programmes suggesting increases in mitochondrial content Holloszy. In plant cells there are structures known as.

Cellular Respiration Study Guide Ck 12 Foundation
202 outlines the process of anaerobic respiration in muscle cells.

. Class 11 Biology Chapter 14- Respiration in Plants deals with the study of the process of respiration and the release of energy for growth in plants. Contractile tissue is able to generate tension of force. Although aerobic respiration is the slowest system to produce energy it provides nearly 95 of all ATP during light exercise or rest.
Each of these stages break down glucose further producing metabolites needed for the other phases to work. Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway and an anaerobic energy source that has evolved in nearly all types of organisms. D E 2 ii What is the role of compound D in anaerobic respiration.
Connected Teaching and Learning from HMH brings together on-demand professional development students assessment data and. This type of respiration takes place in the complete absence of oxygen. The muscle cells require an adequate supply of oxygen for respiration.
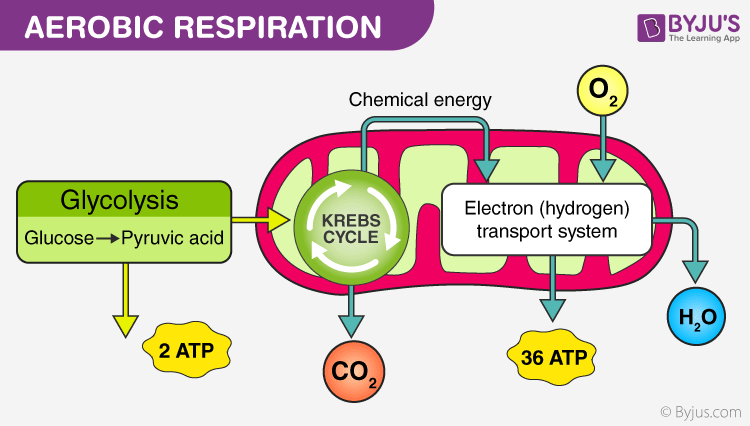
Aerobic respiration consists of glycolysis the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. The mitochondria are often called the powerhouse of the cell because they are responsible for making cellular energy through aerobic respiration. Complete oxidation of organic substances in presence of oxygen takes place.
Aerobic metabolism occurs when oxygen is present while anaerobic respiration occurs when tissue is deprived of oxygen. Predict the changes that would occur at the cellular level when a moss dries out. Learn more about its.
Describe the process of glycolysis and where it occurs. Compared to aerobic respiration sulfate reduction is a relatively energetically poor process though it is a vital mechanism for bacteria and archaea living in oxygen-depleted sulfate-rich environments. Then the chapter discusses the meaning of aerobic respiration and the process of Glycolysis.
Glucose reservoirs and lactate recycling allow the heart to function even during malnutrition. Sulfate reduction is a type of anaerobic respiration that utilizes sulfate as a terminal electron acceptor in the electron transport chain. Skeletal muscle is an excitable contractile tissue responsible for maintaining posture and moving the orbits together with the appendicular and axial skeletonsIt attaches to bones and the orbits through tendons.
Connected Teaching and Learning. If insufficient oxygen is available the cells must respire anaerobically. Name one organelle that you would expect to find in large numbers in a mucus-secreting cell and describe its role in the production of mucus.
Aerobic metabolism accounts for nearly all of the metabolic function in the heart but anerobic metabolism may contribute as well. The chapter begins with the concepts of respiration cellular respiration and the respiratory quotient. I Identify the compounds labelled D and E in Fig.
Aerobic exercise is a type of physical activity that uses your large muscle groups and stimulates your cardio output. Another name for the process is the Embden-Meyerhof pathway in honor of the major contributors towards its discovery and understanding1 Although it doesnt require oxygen hence its purpose in anaerobic respiration it is also the first step in. Excitable tissue responds to stimuli through electrical signals.

Cellular Respiration Review Article Khan Academy
No comments for "Describe the Role of the Following in Aerobic Cellular Respiration"
Post a Comment